Troubleshooting Code Generation Errors
There are two distinct stages in the process of generating output from a template, which is also known as template transformation.
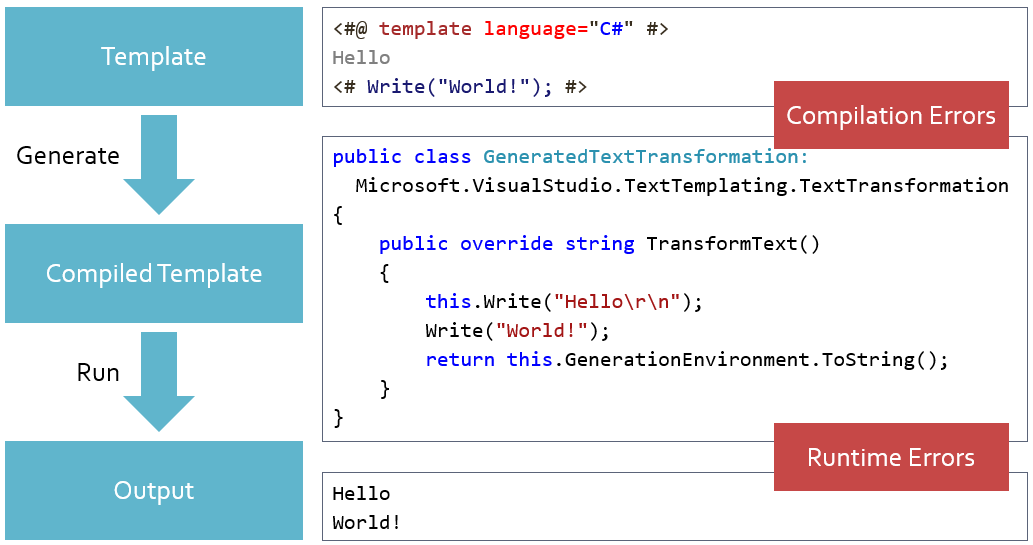
During the first stage, the T4 engine parses the template, uses its text blocks, code blocks and directives
to create a special class called GeneratedTextTransformation and compiles it in a temporary .NET assembly. Errors that
may occur during this stage include those detected by the engine in the template syntax and those detected by the compiler
when compiling the GeneratedTextTransformation.
During the second stage, the engine creates an instance of the GeneratedTextTransformation class, calls its TransformText
method and saves the string it returns to the output file. Errors that occur during this stage are exceptions thrown by code
in the GeneratedTextTransformation when it is running.
Troubleshooting Compilation Errors
Open the Products_Delete.tt template (created in the previous part of this
tutorial) in Visual Studio. As you may recall, it’s a code generation script that produces a DELETE stored procedure using
table schema information retrieved from SQL server using SMO.
- Simulate a parsing error by misspelling one of the
assemblydirectives asassembl.
<#@ assembl name="System.Xml" #>
- Save the template file or select the Run Custom Tool item from context menu in the Solution Explorer to trigger template transformation.
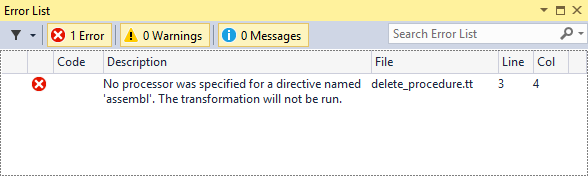
The T4 engine reports errors in the Error List window of Visual Studio. Compilation errors, like this one, include information about the file and the line where it occurred. You can double-click the error in the Error List to quickly jump to the location where it occurred in the template source code.
- Correct spelling of the
assemblydirective, save the template file and verify that the compilation error disappears from the list.
Troubleshooting Runtime Errors
- Simulate a runtime error by assigning
nullto theservervariable. This should trigger a run-time exception in the call to Database constructor.
<#
Server server = null;
var database = new Database(server, "Northwind");
var table = new Table(database, "Products");
table.Refresh();
#>
- Save the template file or select the Run Custom Tool item from context menu in the Solution Explorer to trigger template transformation.
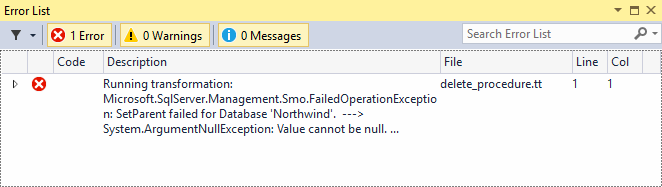
Runtime errors are reported as exceptions converted to string. Note that the Line number for this error doesn’t point to the
actual location of this error. Although the File column shows correct file name in this case, it will not be correct for runtime
errors that occur in a template file referenced from another file with the include directive.
Only the first line of the exception string is reported by default. You can see additional details, including stack trace of the exception in the tooltip window. You can also see it in the Error List window itself by clicking the arrow in the Show Details column.
Running transformation: Microsoft.SqlServer.Management.Smo.FailedOperationException: SetParent failed for Database 'Northwind'.
---> System.ArgumentNullException: Value cannot be null. Parameter name: newParent
at Microsoft.SqlServer.Management.Smo.SqlSmoObject.SetParentImpl(SqlSmoObject newParent)
--- End of inner exception stack trace ---
at Microsoft.SqlServer.Management.Smo.SqlSmoObject.SetParentImpl(SqlSmoObject newParent)
at Microsoft.SqlServer.Management.Smo.Database..ctor(Server server, String name)
at Microsoft.VisualStudio.TextTemplating1805C519B2FAC658A6E510DC975FFA981A1ED7152FBCE.GeneratedTextTransformation.TransformText()
By default, only method names are included in the stack trace. You can enable additional diagnostics by transforming the template in debug mode.
<#@ template language="C#" debug="true" #>
- Set
debugparameter of thetemplatedirective totrue. - Save the template file or select the Run Custom Tool item from context menu in the Solution Explorer to trigger template transformation.
Running transformation: Microsoft.SqlServer.Management.Smo.FailedOperationException: SetParent failed for Database 'Northwind'.
---> System.ArgumentNullException: Value cannot be null. Parameter name: newParent
at Microsoft.SqlServer.Management.Smo.SqlSmoObject.SetParentImpl(SqlSmoObject newParent)
--- End of inner exception stack trace ---
at Microsoft.SqlServer.Management.Smo.SqlSmoObject.SetParentImpl(SqlSmoObject newParent)
at Microsoft.SqlServer.Management.Smo.Database..ctor(Server server, String name)
at Microsoft.VisualStudio.TextTemplating1805C519B2FAC650C07B7524AFFA981A1ED7152FBCE.GeneratedTextTransformation.TransformText()
in c:\Git\olegsych\T4Toolbox\ClassLibrary1\ClassLibrary1\delete_procedure.tt:line 10
Note that the exception stack trace now includes the file name and the line number pointing to the exact location where the error has occurred. This will help you to find and fix simpler runtime errors. In more difficult cases, when the cause of the error is not as obvious, you may need to debug the template by selecting the Debug T4 Template item from the context menu in Solution Explorer.
Troubleshooting Obscure Compilation Errors
Transforming the template in debug mode can also help troubleshoot some of the obscure template compilation errors, because
the T4 engine saves the source code of GeneratedTextTransformation to a temporary file which you can take a look at.
- Open the most recently modified .cs file from the
%TEMP%directory on your computer.